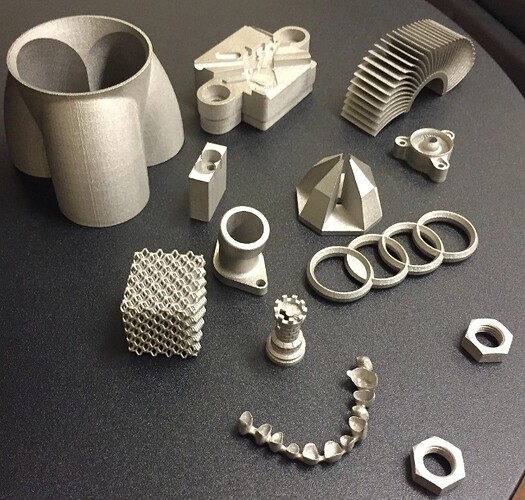
3D printing with brass lets you make detailed and tough items, from jewelry to mechanical parts. Metal 3D printing is really taking off for everything from manufacturing to aerospace, automotive, marine, and construction, with materials like steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium alloys.
But when it comes to brass—a mix of copper and zinc—it can be a bit more complicated. Getting good results with brass requires knowing the best techniques and keeping some key considerations in mind.
Let’s started!
Part 1: 3D Printed Brass and Brass Filled Filament Options
For those looking to mimic this effect using filament, brass-filled filaments are a compelling choice.
For instance, ProtoPasta’s Brass-Filled Metal Composite HTPLA—containing up to 70% real brass powder—produces parts that can be polished to a bright finish.
Other options include copper-filled PLA from formFutura and bronze-filled composites from Virtual Foundry, though some require additional post-processing to remove the PLA base and consolidate the part into 100% metal.
Together, these materials expand the creative potential of 3D printed brass, making high-end metal finishes accessible for a wide range of applications.
Part 2: 3D Printed Brass: An Affordable, Versatile Alloy

Brass, part of the copper family along with bronze, is prized for being less corrosive than copper and more affordable than bronze. This makes it ideal for 3D printed brass applications, from jewelry plating to historical reproductions like plaques, door knockers, and architectural elements.
Applications & Benefits
Brass is commonly used as a base for gold plating, providing a cost-effective alternative to solid gold jewelry. Its ease of machining and attractive finish also make it popular for brass-plating 3D printed metals and polymers, enhancing both aesthetics and durability.
Advanced 3D Printing with Brass
Metal 3D printing using brass opens new doors in manufacturing, automotive, marine, and construction industries. The versatile alloy, known for its corrosion and high-temperature resistance, conductivity, and machinability, has long been used in heat exchangers, musical instruments, pipe fittings, locks, and even ammunition casings. Notably, Italian 3D printer maker 3D4MEC introduced the world’s first specialized laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) 3D printer for brass powders—the 3D4Brass printer, qualified for CuZn42 (CW510) brass powder printing. This breakthrough offers faster, cheaper production of traditionally brass-made parts with improved detail and finish.
3D Printing Brass Method
Brass objects are typically produced using indirect 3D printing methods, as direct printing is challenging due to brass’s properties. The common approaches include:
Lost-Wax Casting: This traditional method involves printing a wax model of your design, which is then encased in a ceramic shell. The wax is melted away, leaving a mold that is filled with molten brass. This technique is ideal for detailed designs and is commonly used in jewelry making.
Metal Filament Printing: For desktop 3D printers, brass-infused filaments are available. These filaments are typically a mix of PLA plastic and fine brass powder. After printing, the object can be polished to reveal a metallic sheen, giving the appearance of solid brass.
For a visual demonstration of 3D printing with brass, you might find this video helpful:
Brass 3D Printing Service: Get Your Designs Printed
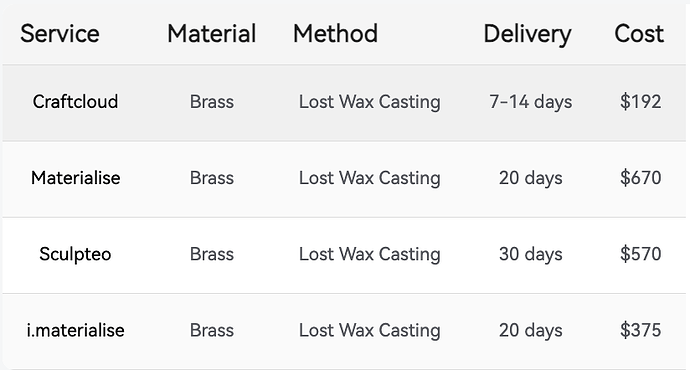
To create brass parts through a 3D printing service, the most common method is lost wax casting. This process involves printing your part in a wax material, covering it in plaster, and then melting the wax out to leave a hollow mold. Once the mold is created, molten brass is poured into it, and afterward, the plaster is broken away once the brass has set. The final step is polishing the brass to achieve the desired finish. Several 3D printing services offer brass printing using this lost wax casting technique. You can easily upload your digital design and get a quote for the process.
3D printed brass, made from a copper and zinc alloy, offers the intricate detail and stunning finish of precious metals at a fraction of the cost, making it ideal for miniatures, sculptures, and jewelry. It provides a versatile alternative to silver and gold, with finishing options that let you polish parts to a mirror shine or achieve a naturally rustic look.
Conclusion
By carefully selecting the appropriate printing method, considering design specifications, and applying proper post-processing techniques, you can achieve high quality brass 3D prints suitable for a variety of applications.